The crypto derivatives landscape is transforming rapidly, with perpetual swaps becoming the dominant trading instrument for leveraged exposure. As both centralized exchanges (CEXs) and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) compete for market share, traders face a critical decision: which platform delivers superior execution, security, and value.
Two fundamentally different approaches have emerged. CEXs offer familiar infrastructure with deep liquidity and sophisticated execution, but require trust and custody surrender. DEXs provide self-sovereign trading with complete transparency and asset control, though they introduce technical considerations and evolving liquidity dynamics.
As the DeFi ecosystem matures, traders need platforms that deliver both performance and principles. Understanding the core differences between DEX and CEX perpetual trading enables informed decisions about custody models, execution quality, and risk management. If you're seeking strategic insight into decentralized perpetual trading that delivers transparency, global access, cost efficiency, and autonomous control, here's why mastering both approaches is essential for modern crypto trading.
What Are Perpetual Swaps?
A perpetual swap is a derivative instrument that enables traders to speculate on asset price movements without expiration dates. Unlike traditional futures contracts, perpetual contracts can be maintained indefinitely through three core mechanisms:
Index Price: A benchmark calculated from multiple spot exchanges to represent the asset's authentic market value and eliminate manipulation from individual venues.
Mark Price: The reference price used for PnL calculations and liquidation triggers, derived from the index price with adjustments for current funding rates to prevent unfair liquidations from temporary price anomalies.
Funding Rate: Periodic payments exchanged between long and short positions that maintain the perpetual's price alignment with spot markets. When the perp trades above the index, longs compensate shorts; when below, shorts compensate longs.
This funding mechanism creates continuous arbitrage opportunities that naturally align the perpetual's price with underlying spot markets, making perps the preferred instrument for leveraged crypto trading without expiration concerns.
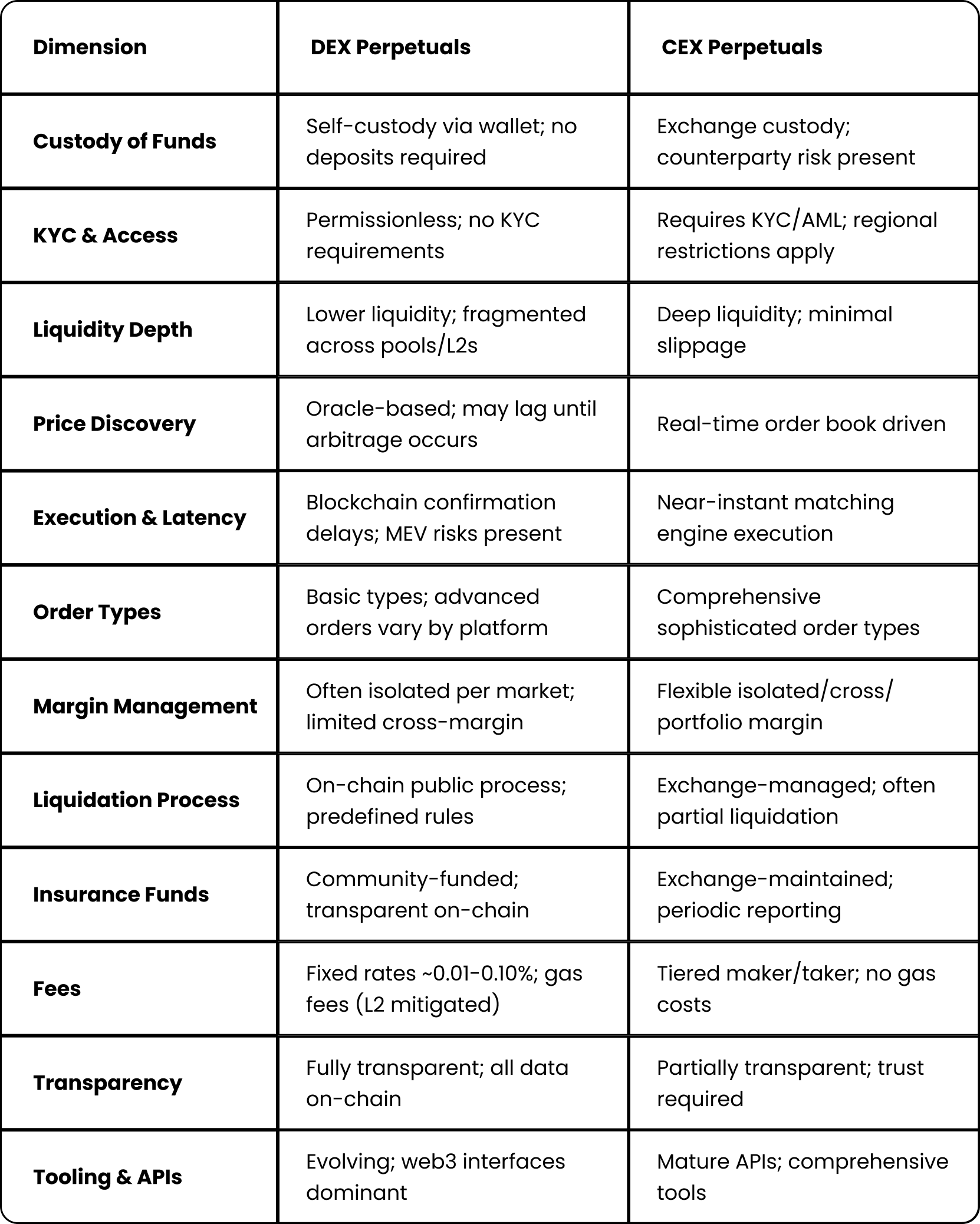
Perpetual Trading DEX vs CEX: Core Differences
Trading perpetual swaps on decentralized exchanges versus centralized exchanges involves fundamental differences in asset custody, trade execution, and risk management approaches.
Custody and Counterparty Risk
CEX: Traders deposit assets into exchange custody, creating counterparty risk from potential platform failures. Benefits include cross-collateralization capabilities and instant internal transfers, but traders depend entirely on platform integrity and regulatory oversight.
DEX: Traders maintain self-custody through blockchain wallets, eliminating exchange default risk while facing smart-contract risk from potential code vulnerabilities. Reduced collateral flexibility but complete asset sovereignty.
Why it matters: This represents the fundamental trade-off between operational convenience and financial sovereignty. CEX users risk total asset loss from exchange failures, while DEX users face technical risks but maintain complete control.
Liquidity, Depth, and Execution Quality
CEX: Concentrated order-book liquidity from market makers creates tight spreads and minimal slippage with sub-millisecond execution capabilities. Risk of liquidity evaporation during extreme volatility or platform outages.
DEX: Generally lower liquidity concentrations with wider spreads and higher slippage potential. MEV risks from sandwich attacks and latency from block confirmation times. Layer 2 solutions are significantly improving execution performance.
Why it matters: Execution quality directly impacts trading profitability and strategy viability. CEXs excel for active trading strategies, while DEXs suit position-based approaches but are rapidly closing performance gaps.
Pricing, Oracles, and Funding Mechanics
CEX: Controls internal mark price calculations with real-time updates and sophisticated risk management systems. Funding rates computed and charged automatically without external dependencies.
DEX: Relies on external oracle networks like Chainlink or Pyth for pricing data, creating potential delays or manipulation vulnerabilities. Implements protective safeguards including TWAP smoothing and circuit breakers.
Why it matters: Pricing accuracy affects liquidation fairness and funding costs. CEX pricing offers responsiveness but opacity, while DEX pricing provides transparency at the cost of potential oracle delays.
Liquidations, Insurance Funds, and ADL
CEX: Risk engines attempt partial liquidations initially with substantial insurance fund backing. Auto-Deleveraging (ADL) mechanisms used only during extreme market events.
DEX: Smart contracts execute automatic liquidations when triggered by network participants. Community-funded insurance funds maintain transparency but may implement social loss mechanisms if depleted.
Why it matters: CEX liquidations can be more accommodating, while DEX liquidations are predictable but mechanical. DEX transparency enables real-time insurance fund health verification.
Fees: Maker/Taker, Gas, and Rebates
CEX: Traditional maker/taker structures with volume-based discounts and potential rebates for market makers. No blockchain costs but withdrawal fees apply.
DEX: Fixed trading fees plus gas costs, though Layer 2 solutions have minimized this burden. Some platforms like ApeX Protocol eliminate gas entirely through subsidized architectures.
Why it matters: Total cost structures determine strategy profitability. Layer 2 adoption has made DEX trading cost-competitive with CEXs for most applications.
Comparison Table
How to Trade Perpetuals Decentralized
Trading perpetuals on DEXs requires combining DeFi expertise with disciplined trading methodology. Here are proven practices for decentralized perpetual trading while managing risks and optimizing costs:
Choose Liquid Pairs & Optimal Timing: Focus on perpetuals with robust liquidity (typically major assets like BTC, ETH, or those with substantial liquidity mining support). Even established DEXs can have shallow books for lesser-known assets. Trade during peak activity periods when liquidity is abundant and oracle updates are frequent to minimize slippage and pricing delays.
Apply Conservative Leverage: Use moderate leverage on DEXs, particularly during volatile market conditions. On-chain trade execution means sudden price movements can trigger liquidations faster than reaction times allow. Conservative approaches (3x–5x leverage depending on asset volatility) provide adequate buffers against oracle or pricing delays.
Utilize Limit Orders & TWAP Strategies: Employ limit orders or post-only modes to avoid unnecessary taker fees and slippage. Some DEX interfaces enable limit orders that execute on-chain at specified prices. For substantial orders, consider splitting them into smaller tranches over time using Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) strategies to prevent excessive order book impact and dodge MEV bots targeting large transactions.
Implement Careful Stop-Loss Management: Risk management remains paramount. Use stop-loss orders where DEX platforms support them (platforms like GMX or dYdX offer trigger order functionality). Remember that on-chain stop-losses depend on oracle prices and transaction execution, which may lag during market crashes. Set stops more conservatively than on CEXs to account for these delays.
Monitor Funding & Oracle Dynamics: Track current funding rates and upcoming payment schedules. Unusually high funding rates might influence position holding decisions through funding periods. Understand your DEX's oracle update frequency—sudden market movements within update windows could temporarily expose positions to margin risks.
Prepare for Gas Cost Variations: Maintain adequate native token balances for gas payments, especially with active positions. During volatile periods, gas prices can spike due to network congestion. Include gas budgeting in your trading strategy. While L2 platforms reduce this concern, maintaining cost buffers remains prudent.
Avoid Low-Liquidity Periods: Exercise caution during known illiquid periods or before major news releases. After significant economic announcements, even CEX order books can thin—DEX liquidity providers may withdraw capital or widen ranges during these times. Consider reducing leverage or diversifying across venues to mitigate single-platform risks.
Leverage Analytics & Alert Systems: Utilize comprehensive analytics tools provided by DEX platforms. Many display real-time open interest, long/short ratios, and funding rate charts indicating market sentiment. Establish price alert systems monitoring DEX prices, as they can temporarily decouple from CEX prices. Advanced DEXs like ApeX integrate AI-driven tools (Alpha Radar for on-chain and social data analysis) providing decentralized traders competitive advantages in momentum identification and risk assessment.
Worked Examples: All-In Trading Cost
To illustrate these concepts, let's examine two scenarios calculating comprehensive trade costs on DEX versus CEX platforms, including all components: slippage, fees, funding, and gas expenses.
Example A: DEX Trade (Taker on L2) A trader executes a long position on 1 BTC perpetual at $30,000 via a DEX on Arbitrum, submitting a market order consuming available pool/order book liquidity.
Slippage: Trade incurs slippage from finite liquidity—average execution price increases 0.05% above initial quote. 0.05% of $30,000 equals $15 slippage (approximately 5 basis points of price impact).
Trading Fee: DEX charges 0.1% taker fee on $30,000 notional, totaling $30 (10 basis points).
Gas Cost: Arbitrum gas costs approximately 0.001 ETH. At $1,800 per ETH, gas expense equals $1.80 (roughly 0.6 basis points of trade size).
Funding: Funding rate at next interval is +0.01% (longs compensate shorts over 8 hours). Maintaining position through one funding period costs 0.01% on $30,000, equaling $3.
Total costs: $49.8 (16.6 basis points). BTC requires approximately 0.166% appreciation to $30,050 for break-even after 8 hours.
Example B: CEX Trade (Maker on CEX) A trader places a limit order for 1 BTC perpetual at $29,970 on a centralized exchange, slightly below current $30,000 market price. Order fills as market briefly dips.
Spread Advantage: As maker, trader avoids crossing spreads and gains price improvement. Approximately $10 savings compared to market taking by entering below market price.
Trading Fee: Trader pays 0.02% maker fee on $29,970 notional, equaling $5.99.
Gas Costs: No blockchain fees apply to CEX trades.
Funding: Same +0.01% funding rate over 8 hours costs approximately $3.
Net cost calculation: ($6 + $3 – $10) = –$1. Spread advantage covers fees and funding, achieving essentially 0% break-even requirement.
Key Insight: DEX taker required approximately 17 basis points of favorable price movement for break-even; CEX maker required essentially 0 basis points. This demonstrates how execution methodology and venue liquidity dramatically influence trading costs. Always estimate these components beforehand to ensure expected price movements exceed total trading expenses.
Conclusion
Perpetual swaps represent powerful instruments for expressing leveraged views on crypto assets without expiration constraints. The choice between DEX and CEX perpetual trading involves weighing autonomy against convenience, transparency against performance. CEXs provide familiar infrastructure with deep liquidity and sophisticated execution, but demand trust and compliance. DEXs embody financial sovereignty principles, enabling global access and transparent operations, while introducing technical considerations and evolving liquidity landscapes.
Effective mitigation strategies exist for DEX limitations (Layer 2 networks, improved oracles, execution optimizations) and CEX risks (reputable regulated platforms, insurance solutions). Sophisticated traders often employ both approaches, capitalizing on respective strengths.
As you explore decentralized perpetual trading, apply the same professionalism and risk management discipline used on centralized platforms. Calculate comprehensive costs, utilize appropriate tools for each situation, and avoid excessive leverage simply due to accessibility. With informed strategies and risk awareness, you can harness the unique advantages each venue offers.
Regardless of platform selection, always implement disciplined risk controls and thorough due diligence before capital deployment. Crypto markets reward preparation—manage leverage responsibly, protect against adverse scenarios, and continuously refine approaches in this dynamic trading environment.
Trade Smarter with ApeX Omni Unlock the full potential of decentralized trading on ApeX Omni. From crypto perpetuals and spot markets to U.S. stocks and prediction markets, everything you need is in one place. With deep liquidity, powerful trading tools, and zero gas fees, ApeX Omni makes it easy to build and execute strategies that match your trading style.
Earn While You Learn — $100 USDT Per Quest Your trading knowledge can now pay off. Join our Learn & Earn series on Galxe, where each quick quiz you complete rewards you with $100 USDT.
Simply connect your wallet to ApeX Omni, take the quiz, and claim your reward. Fast, simple, and designed to help you grow while you earn.

